
Essential Cybersecurity Guide for Victorian Law Firms: Meeting VLSBC Minimum Cybersecurity Expectations

Duong Dang
29 June 2025
Table of Contents
Cybersecurity is critical for law firms due to the sensitive client data they handle. The Victorian Legal Services Board + Commissioner (VLSBC) has set minimum cybersecurity expectations to ensure law practices protect this data and meet their legal obligations. This guide details these requirements, focusing on immediate critical controls, technical system controls, and human-focused behavioural controls. Implementing these measures helps prevent financial losses, reputational damage, legal penalties, and operational disruptions. By following this guide, law firms can enhance their security posture, comply with regulations, and maintain client trust.
Introduction
Every 6 minutes, a cyberattack happens in Australia, making law firms with sensitive client data prime targets. The Victorian Legal Services Board + Commissioner (VLSBC) has established minimum cybersecurity expectations to protect this data and uphold professional standards. Failing to meet these requirements can have devastating consequences. This guide helps you understand and implement VLSBC's cybersecurity measures, ensuring your firm's protection and compliance.
Why Cybersecurity Matters for Law Firms
Law firms hold confidential information, making them lucrative targets for cybercriminals. A breach can cause financial loss, reputational damage, legal penalties, and operational disruption.
A cyberattack can cripple a law firm, leading to:
Financial Loss
Ransomware attacks, data breaches, and fraud can result in significant financial losses.
Reputational Damage
A security incident can erode client trust and severely tarnish your firm's reputation.
Legal and Regulatory Penalties
Non-compliance with VLSBC requirements can result in disciplinary action, fines, and potential legal liability.
Operational Disruption
Cyberattacks can grind your firm's operations to a halt, causing downtime, lost productivity, and client dissatisfaction.
VLSBC Minimum Cybersecurity Expectations
Summary of Key Points
39 Cybersecurity Instances can be seen as conduct capable of Unsatisfactory Professional Conduct (UPC) or Professional Misconduct (PM).
56 Cybersecurity Expectations are outlined by the VLSBC.
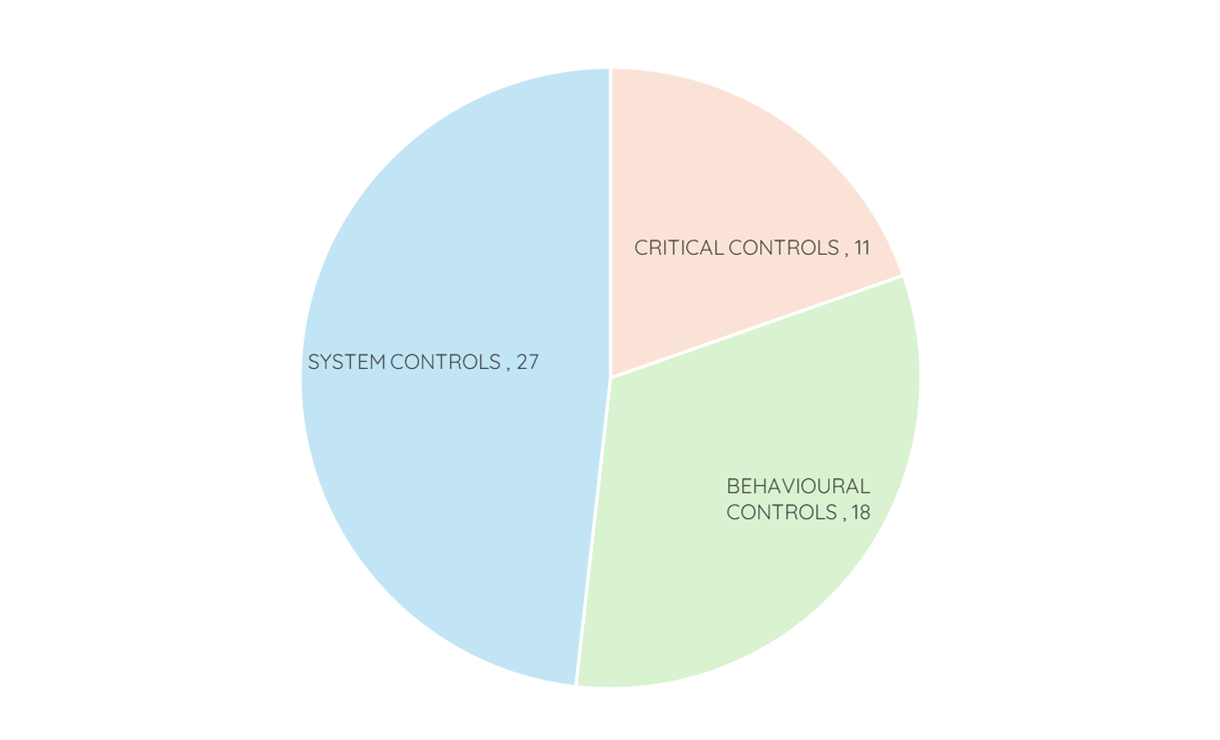
The VLSBC's minimum cybersecurity expectations span three key areas:
11 Critical Controls should be implemented immediately if not already completed. Work with your IT team or seek our assistance.
27 System Controls focus on the technical safeguards within your systems. Collaborate with your IT team or get support from us to implement these.
18 Behavioural Controls highlight the human element of cybersecurity. This includes client protection, incident response, and cybersecurity awareness training, which require active participation from your team and IT provider.
each playing a crucial role in your firm's cybersecurity posture.
Critical Controls (Highest Priority)
These controls should be implemented immediately if not already in place. Work with your IT team or contact CyberOxide for assistance.
Cybersecurity Area | VLSBC Expectations | Conduct Capable of Constituting UPC or PM | Cybersecurity Importance |
Security updates | - Keep all work devices, apps, and software up-to-date with the latest security patches. - Turn on automatic updates where available. | - Failing to install security updates and patches. - Not turning on automatic updates. | Ensures that vulnerabilities in software and devices are patched promptly, reducing the risk of exploitation by cybercriminals. |
Passwords and logins | - Use strong, unique passwords for all devices and accounts. - Don't reuse passwords. - Consider using a password manager. | - Using weak or common passwords. - Reusing passwords. - Storing passwords insecurely. | Strong passwords and unique credentials protect against unauthorised access, ensuring only authorised individuals can access sensitive information. |
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) | - Turn on MFA for all online accounts and services where available. - Follow online guides to enable MFA. | - Not enabling MFA. - Sharing MFA codes with others. - Ignoring MFA alerts of suspicious attempts. | MFA adds an extra layer of security, significantly reducing the likelihood of unauthorised access even if passwords are compromised. |
System Controls
These controls focus on securing your systems. Collaborate with your IT team or seek help from CyberOxide to implement them.
Cybersecurity Area | VLSBC Expectations | Conduct Capable of Constituting UPC or PM | Cybersecurity Importance |
Security software | - Install and enable security and antivirus software on all work devices. - Perform regular virus and malware scans. - Use a secure Domain Name System (DNS) provider. | - Using outdated software. - Not performing regular scans. - Using unsecure DNS providers. | Ensures that threats are detected and mitigated promptly, preventing malware infections and unauthorised access. |
Access control | - Grant different levels of access based on job roles. - Regularly review permissions. - Don't use shared accounts. | - Giving access beyond job requirements. - Not reviewing access permissions. - Using shared accounts. | Limits access to sensitive information to authorised personnel only, reducing the risk of internal and external threats. |
Backups | - Regularly back up data to avoid data loss. - Encrypt backups. - Test backups to ensure they are successful. | - Not backing up data. - Storing backups unencrypted. - Failing to test backup restorations. | Ensures data can be restored in case of cyberattacks, system failures, or accidental deletions, minimising downtime and data loss. |
Information security | - Encrypt sensitive data at rest and in transit. - Use secure communications for high-risk information. - Secure physical storage of sensitive data. | - Storing data on unencrypted drives. - Using unsecure communication channels. - Failing to secure physical storage. | Protects data from being intercepted or accessed by unauthorised individuals, maintaining confidentiality and integrity. |
Behavioural Controls
These controls address the human element of cybersecurity. Work closely with your IT provider to ensure implementation and engage your team.
Cybersecurity Area | VLSBC Expectations | Conduct Capable of Constituting UPC or PM | Cybersecurity Importance |
Training | - Provide cybersecurity training at induction and yearly. - Update training to address new threats. | - Not providing up-to-date training. - Failing to educate staff on cybersecurity protocols. | Empowers staff with the knowledge to recognise and respond to cyber threats, reducing the risk of human error leading to security incidents. |
Client or bank verification | - Implement procedures to verify client details before making transactions. - Ensure staff are familiar with verification procedures. | - Not verifying client or bank details before transactions. - Ignoring verification protocols. | Prevents fraudulent transactions and ensures the integrity of client interactions by verifying the authenticity of clients and financial details. |
Incident response and reporting | - Create and implement an incident response plan. - Regularly update and test the incident response plan. - Report data breaches promptly. | - Not having an incident response plan. - Failing to report data breaches. - Ignoring plan updates. | Ensures swift and effective action in the event of a cyber incident, minimising damage and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements for breach notification. |
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Disciplinary Action Capable of amounting to unsatisfactory professional conduct (UPC) or professional misconduct (PM).
Financial Penalties Significant fines for non-compliance with data protection laws.
Reputational Damage Loss of client trust and potential damage to reputation.
Implementation Steps
Risk Assessment Identify your firm’s specific vulnerabilities with a comprehensive assessment. CyberOxide offers a free Cybersecurity Health Check to get you started.
Cybersecurity Plan Create a tailored plan outlining security goals, strategies, and timelines for implementing necessary controls.
Implement Security Measures Prioritise implementing critical controls, followed by system and behavioural controls.
Staff Training Regularly train staff on cybersecurity best practices.
Review and Update Continuously update your cybersecurity plan to address new threats and evolving regulations.
Conclusion
Meeting VLSBC cybersecurity requirements is a strategic investment in protecting your law firm's assets, reputation, and client trust. By taking a proactive approach and partnering with a cybersecurity expert like CyberOxide, you can ensure your firm is well-prepared to navigate the complexities of the digital landscape and mitigate the risks of cyber threats.

